animation属性

通过前面的知识点知道cssanimations由关键帧(@keyframes)和css声明两部分构成,接下来学习下动画的声明属性。animation属性用于描述动画的css声明,包括指定具体动画以及动画时长等行为。与transtion类似,animation也是一个复合属性,其取值主要有以下8个,下表格6-5列出了@keyframes规则和所有动画属性:
表6-5 @keyframes规则和所有动画属性
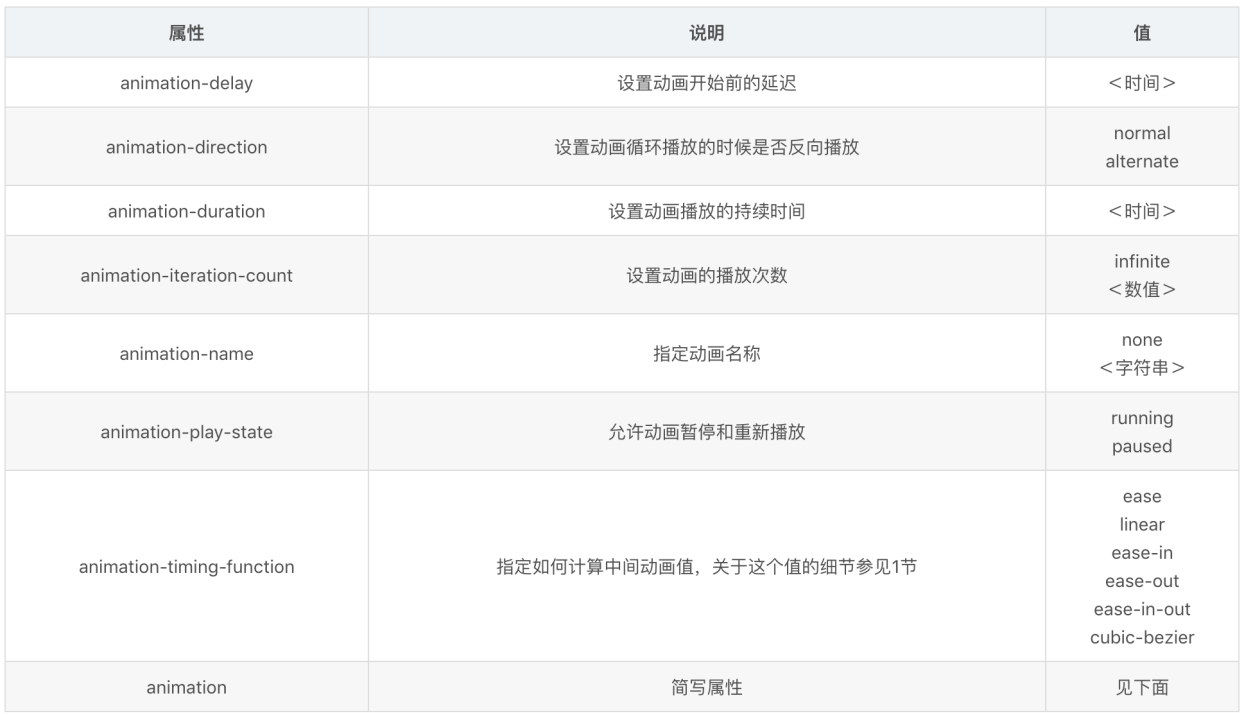
1.animation-name
用来定义一个动画的名称,其主要有两个值,一个是name,是由@keyframes创建的动画名,换句话说此处的name要和@keyframes中的name一致,如果不一致,将不会实现任何动画效果;另一个是none,默认值,当值为none时,将没有任何动画效果,另外,该属性可以同时附多个animation的名称给一个元素,只需要用逗号“,”隔开,可以实现更多且不同的动画效果。
2.animation-duration
用来指定元素播放动画所持续的时间长,也就是完成从0%到100%一次动画所需要的时间,取值<time>为数值,单位为s(秒),其默认值为0。
3.animation-timing-function
animation-timing-function属性用来设置动画播放方式,指元素根据时间的推进来改变属性值的变换速率,其取值与作用同transition属性一致。
4.animation-delay
用来指定元素播放动画开始时间,取值<time>为数值,单位为s,默认值为0。
5.animation-iteration-count
用来指定元素播放动画的循环次数,取值<number>可以为数字,其默认值为“1”;infinite为无限次数循环。
6.animation-direction
用来指定元素动画播放的方向,其只有两个值,默认为normal,如果设置为normal,动画的每次循环都是向前播放;另一个值是alternate,作用是,动画播放在第偶数次向前播放,第奇数次向反方向播放。
通过案例6-16来体验div尺寸由小到大,然后由大到小。
例6-16 example16.html
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>动画animation-direction属性</title> <style type="text/css"> @-webkit-keyframes 'testAnimationDirection' { /*from{} 动画开始时的设置,也可以使用0%*/ 0% {width: 50px;} 20% {width: 100px;} 40% {width: 150px;} 60% {width: 200px;} 80% {width: 250px;} /*to{} 动画结束时的状态,也可以使用100%*/ 100% {width: 300px;} } div{ width: 50px;height: 50px;border:1px solid red; -webkit-animation-name:'testAnimationDirection'; /*动画名称*/ animation-duration: 10s; /*动画所持续的时间*/ -webkit-animation-timing-function: ease-in-out; /*动画播放方式,这个属性要使用前缀*/ animation-delay: 0s;/*动画开始时间*/ -webkit-animation-iteration-count: infinite; /*动画播放循环次数:infinite(无限次循环),这个属性要使用前缀*/ animation-direction: alternate; /*动画播放方向,alternate(偶数次向前,奇数次向反方向)*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div></div> </body> </html> |
7.animatiob-play-state
用来控制元素动画的播放状态,其有running和paused两个值,其中running为默认值,它的作用就类似于音乐播放器,可以通过paused将正在播放的动画停下来,也可以通过running将暂停的动画重新播放。但这里的重新播放不是从元素动画的开始播放,而是从暂停的那个位置开始播放,另外,如果暂停了动画的播放,元素的样式将回到最原始设置状态。(这个属性目前很少内核支持,所以只是稍微提一下), 通过案例6-17来体验控制元素动画的播放状态,当鼠标移除离开div时,小方块暂停移动,元素的样式回到最原始设置状态。效果如图6-20所示。
例6-17 example17.html
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style> @keyframes move { 0%{transform: translateY(90px);} 15%{transform: translate(90px,90px);} 30%{transform: translate(180px,90px);} 45%{transform: translate(90px,90px);} 60%{transform: translate(90px,0);} 75%{transform: translate(90px,90px);} 90%{transform: translate(90px,180px);} 100%{transform: translate(90px,90px);} } div {width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;margin: 20px auto; } span {display: inline-block; /*行内块元素*/ width: 20px;height: 20px;background: orange; transform: translateY(90px); /*垂直方向移动*/ animation-name: move; /*动画名称*/ animation-duration: 10s; /*动画持续时长*/ animation-timing-function: ease-in; /*播放方式:加速*/ animation-delay: 0.2s; animation-iteration-count:infinite; /*循环次数:无限循环*/ animation-direction:alternate; /*播放方向*/ animation-play-state:paused; /*播放状态:正在播放的动画停下来*/ } div:hover span { /*暂停的动画重新播放*/ animation-play-state:running; background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div><span></span></div> </body> </html> |
图6-20 控制元素动画的播放状态
8.animation-fill-mode
规定当动画不播放时(当动画完成时,或当动画有一个延迟未开始播放时)要应用的样式。主要具有四个属性值:none、forwards、backwards和both。其四个属性值对应效果如下表6-6所示。
表6-6 animation-fill-mode
| 值 | 描述 |
| none | 不改变默认行为。 |
| forwards | 当动画完成后,保持最后一个属性值(在最后一个关键帧中定义)。 |
| backwards | 在 animation-delay 所指定的一段时间内,在动画显示之前,应用开始属性值(在第一个关键帧中定义)。 |
| both | 向前和向后填充模式都被应用。 |
属性详解:
none,animation-fill-mode:none时,默认值,不改变元素默认行为,使用的动画不会对动画等待和动画完成的元素样式产生改变。
forwards,animation-fill-mode:forwards;当使用这个值时,告诉浏览器动画结束后,元素的样式将设置为动画的最后一帧的样式。
backwards和forwards效果不一样,如果设置为backwards值,那么在动画等待的那段时间内,元素的样式将设置为动画第一帧的样式。
从技术上讲,每一个动画都有一个默认的延迟时间,只不过这个时间是0而已,所以你并没有看到其中的变化。根据前面对backwards的描述:动画等待的那段时间内,元素的样式将设置为动画第一帧的样式。这样解释你就应该较为明白,因为我们的示例有一个1s时间的延迟,这样一来,元素在等待的这1s时间内,元素的样式就是关键帧(也就是@keyframes中的frome或0%的样式)第一帧中的样式,通过案例6-18来体验。
例6-18 example18.html
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>animation-fill-mode属性值</title> <style> @-webkit-keyframes 'wobble' { 0% {margin-left: 100px;background: green; /*绿色*/} 40% {margin-left: 150px;background: orange;} 60% {margin-left: 75px;background: blue;} 100% {margin-left: 100px;background: red;} } div{ width: 50px;height: 50px;margin-left:100px;background: blue; -webkit-animation-name:'wobble'; animation-duration: 10s; -webkit-animation-timing-function: ease-in-out; animation-delay: 5s; /*循环次数*/ -webkit-animation-iteration-count: 10; animation-direction: alternate; animation-fill-mode:none; /*动画开始为蓝色*/ /*animation-fill-mode:backwards; /*动画开始为绿色*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div> </div> </body> </html> |
在这个示例中,在延迟的时间内方形变成蓝色。然后在5s时间之后,元素颜色变成动画第一帧的颜色。如果设置为“animation-fill-mode:backwards;”动画等待的那段时间内,元素的样式将设置为动画第一帧的样式为绿色。
利用animation组合属性,也同样可以实现上述属性的设置,如图6-21所示:

图6-21 animation组合属性
由图6-21定义的组合属性可知,这个动画的关键帧名称加“wobble”,动画持续时间为“10s”,使用“ease-in”播放方式,延迟时间为“2s”,无限次来回轮流播放。
动画属性综合案例1:通过案例6-19来体验让一个正方形逐渐变大并变成圆形。该动画不要求移动,循环轮流播放,延迟2s开始,并且使用均匀变换,另外,当鼠标指针悬停在该动画上时,该动画暂停播放,代码实现如下所示:
例6-19 example19.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>方形变圆形</title> <style> div{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #ff7448;margin: 20px auto; /*依次:名称,时长,方向,次数,开始时间,播放方式*/ animation: movediv 3s alternate infinite 2s ease-in-out; } div:hover{animation-play-state: paused;} @keyframes movediv{ from{ /*定义刚开始时的一些处理,通常直接使用原始样式*/ } to{ width: 300px;height: 300px;border-radius: 50%; /*圆角*/ } } </style> </head> <body> <div></div> </body> </html> |
动画属性综合案例2:通过案例6-20来体验div做矩形运行。本实例将完成一个相对更复杂一点的动画。让一个div沿一个矩形路线从左上移动到右上,再移动到右下,再移动到左下,最后回到原点。本实例主要用来解决关键帧更细致的处理问题。代码实现如下所示:
例6-20 example20.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>动画帧的变化</title> <style> body{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;} div{width: 800px;height: 800px;border: 1px solid red;} #mydiv{ width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: #61ff87; left: 0px;top:0px;animation: movediv 5s alternate; } div:hover{ animation-play-state: paused; } @keyframes movediv{ from{} /*动画开始时的设置,也可以使用0%*/ 25%{background-color: #ff79ef;margin-left: 600px;margin-top: 0px;} 50%{background-color: #4249ff;margin-left: 600px;margin-top:600px;} 75%{border: double 2px #0e2218;margin-left: 0px;margin-top: 600px;}/*to表示动画结束时的状态,也可以使用100%*/ to{margin-left: 0px;margin-top: 0px;} } </style> </head> <body> <div><div id="mydiv"></div></div> </body> </html> |
动画属性综合案例3:通过案例6-21来体验实现动漫人物跑动的动画效果。本实例将完成游戏中人物跑动的动画:让一个图片动画人物“跑起来”......。代码实现如下所示:
例6-21 example21.html
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>帧动画(animation)属性</title> <style> /*background-position 属性设置背景图像的起始位置*/ @keyframes myanimation { /* 开始创建动画帧 */ 0%, 8% { background-position: 0 0; } 9.2%, 17.2% { background-position: -140px 0; } 18.4%, 26.4% { background-position: -280px 0 ; } 27.6%, 35.6% { background-position: -420px 0 ; } 36.8%, 44.8% { background-position: -560px 0 ; } 46%, 54% { background-position: -700px 0 ; } 55.2%, 63.2% { background-position: -840px 0 ; } 64.4%, 72.4% { background-position: -980px 0 ; } 73.6%, 81.6% { background-position: -1120px 0 ; } 82.8%, 90.8% { background-position: -1400px 0 ; } 92%, 100% { background-position: -1540px 0 ; } } div { width: 340px;height: 315px;border: 1px solid red; background-image: url('image/run.png');background-size: contain; /* 设置帧动画效果 */ animation-name: myanimation; animation-duration: 2s; animation-timing-function: linear; animation-iteration-count: infinite; animation-fill-mode: backwards; } </style> </head> <body> <div><div> </body> </html>
|



